Possible Causes
Dopamine – The Missing Link
The brain has multiple areas that weigh in on interpreting signals traveling up from the brainstem. The same holds true for the brain’s formulation of a response to incoming transmissions. These brain regions rely on a network of freeways (called the basal ganglia) to facilitate the dialog. And as it turns out, dopamine is the predominant communicating transmitter and its levels are very low in people with fibromyalgia.
Research Findings in Fibro
A proper functioning basal ganglia requires a healthy supply of dopamine for conveying information. When a person is subjected to a painful stimulus, this relay station should pour out dopamine to reduce the impact of the discomfort. In fact, higher dopamine reserves in the basal ganglia correspond to higher pain threshold levels in healthy people.
Low spinal fluid levels of dopamine and reduced pain thresholds in fibromyalgia prompted researchers to look at dopamine levels in the basal ganglia. Brain imaging showed that healthy controls poured out dopamine when subjected to pain. However, this response was blunted in people with fibromyalgia.1 The study illustrates that dopamine release from the basal ganglia in fibromyalgia is disrupted. It also provides an explanation for why the pain processing system is crippled.
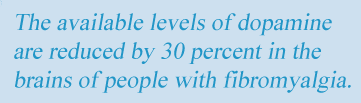
Not only is dopamine a potent analgesic in the CNS, but it also plays an important role in cognition and motivation. In addition, dopamine-transmitting neurons in the brain’s hippocampus help prevent stress responses from spinning out of control. Yet, the available levels of dopamine are reduced by 30 percent in the brains of people with fibromyalgia.2
Studies show dopamine reductions in many brain regions in fibromyalgia patients (including one funded by AFSA). And the low levels aren’t a fluke. Decreased dopamine correlates with the reduced pain thresholds (the lower the dopamine, the lower the pain threshold). Reductions in dopamine also correspond to loss of gray matter in people with fibromyalgia.3 The hippocampus is the hardest hit structure and this helps explain the cognitive dysfunction called fibrofog.
Dopamine Boosting Agents
None of the FDA-approved drugs for fibromyalgia work to increase brain dopamine. And, even if one were to take a dopamine-boosting medication, the high doses required are fraught with side effects. Conversely, drugs that block NMDA receptors can produce pain relief and ease fibrofog by raising dopamine levels. Memantine is a medication in this class that shows promise in fibromyalgia.4 Dextromethorphan (main ingredient in cough syrup) and supplemental magnesium may help too, but more research is needed.
What could be causing impaired dopamine production in fibromyalgia? Research in Parkinson’s patients points to glial cell activation.5 This is an interesting theory, especially since the glia cells are activated in fibromyalgia (see the next article). However, the dopamine-glial cell link in fibromyalgia needs to be further explored.
Stay Current on Treatment & Research News: Sign up for a FREE Membership today!
Medications | FibroFog | Why So Many Symptoms? | More About NMDAs | Finding A Doctor
Back To Central Nervous System Causes
References for Dopamine in Fibromyalgia
- Wood PB, et al. Eur J Neurosci 25(12):3576-3582, 2007. Abstract
- Albrecht DS, et al. Brain Imaging Behav 10(3):829-839, 2016. Free Report
- Wood PB, et al. J Pain 10(6):609-618, 2009. Free Report
- Fayed N, et al. Neuroradiol J 32(6):408-419, 2019. Free Report
- Wang T, et al. Cells 12(19):2336, 2023. Free Report
